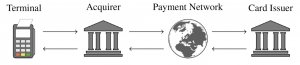
EMV is the global standard for payment with credit cards and used in over 9 billion payment cards worldwide. Most EMV transactions require online authorization by the card issuer. Namely, the merchant’s payment terminal sends an authorization request from its acquirer bank to the card issuer over a payment network, typically operated by the company that brands the card such as Visa or Mastercard, as pictured here:
In a recent work, David Basin, Ralf Sasse and Jorge Toro show that it is possible to induce a mismatch between the card brand and the payment network brand, from the terminal’s perspective. The resulting card brand mixup attack has serious security consequences. In particular, it enables criminals to use a victim’s Mastercard contactless card to pay for expensive goods without knowing the card’s PIN. Concretely, the attacker fools the terminal into believing that the card being used is a Visa card and then applies the recent PIN.
Basin, Sasse and Toro have built an Android application and successfully used it to carry out this attack for transactions with both Mastercard debit and credit cards, including a transaction for over 400 USD with a Maestro debit card. The attacker’s approach is pictured next.

The merchant terminal (1) is linked to the merchant device (2) which sets the price and is used to generate receipts, and at which a customer can pay with a physical credit card or a virtual credit card on a phone, like Apple and Google Pay. The attacker then uses a phone (3) to pay contactlessly at (1), making it look like a standard virtual credit card transaction. However, in reality this phone wirelessly receives the actual card data from their other phone (4) which is held next to the victim’s credit card (5), and no PIN is required.
The attack on Mastercard allows criminals to trick a terminal into transacting with a victim’s Mastercard contactless card while believing it to be a Visa card, with critical consequences. As a result of our disclosure process, Mastercard has since implemented defense mechanisms, which were experimentally confirmed as effective against the attack!
Demo video of the attack and other information are available at https://emvrace.github.io/.
